Case Studies
URBANE partners have designed real-world case studies that cover different agroecological zones in Western Africa. Six WA countries make up the URBANE CS countries and the pilot sites were selected following a series of assessments, registering capabilities and potential impact of the URBANE approach in these farms considering not only environmental factors but also socio-economic ones.
Nigeria
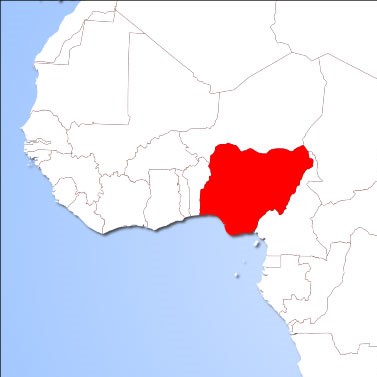
Six pilot sites are selected, two for EACH: vegetable production, poultry and piggery. One of the piggery farms also has some crops being cultivated, offering the possibility of exploring crop-livestock integration.

Morocco
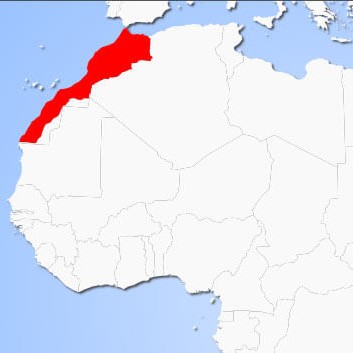
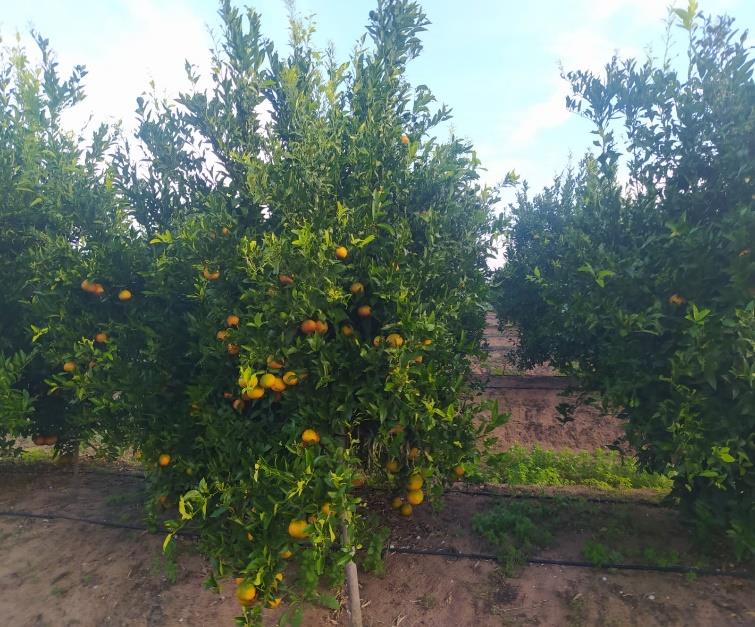
Two PILOT sites are selected to deploy the case study scenarios. The first FARM is an animal farm breeding chickens and the second is a crop farm where CITRUS TREES ARE GROWN.

Senegal
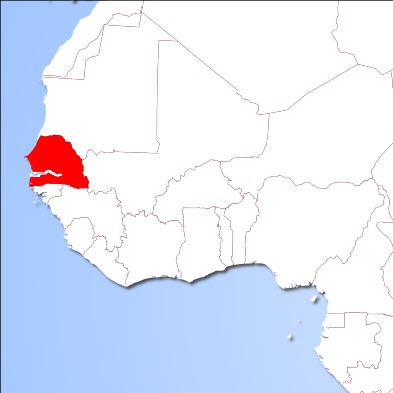
TWO PILOT SITES ARE SELECTED both of which are mixed farms. For the first one agroecological practices are already in use and will be enhanced with urbane, while the second site is a combination of four smaller farms in near proximity that form a collective.

Ghana
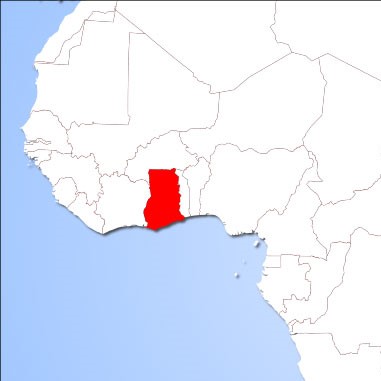
TWo Pilot sites are selected, both of which are piggeries. Potential bat-pig interaction routes will be investigated for identifications of differences in both likelihood of bat virus spill-over into pigs and pig-to-pig transmission of bat viruses in intensive vs. extensive farming systems.

Benin
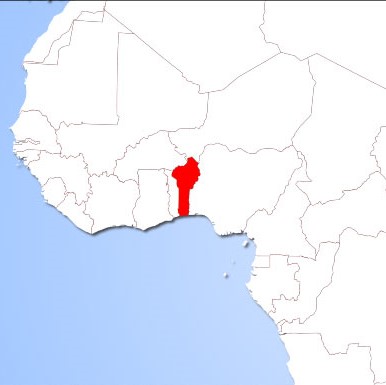
Four pilot sites are selected, two for crop farming and two for poultry breeding. The case study will be focused on local mixed farming systems where intensive farming practices are currently applied with uses of pesticides and chemical fertilizers.

Burkina Faso
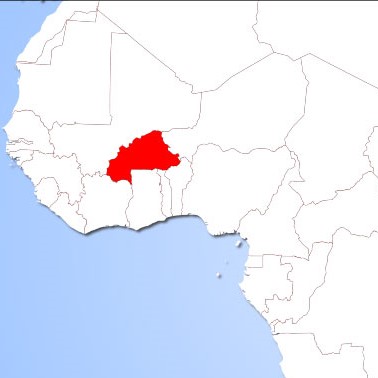
TWO PILOT SITES ARE SELECTED. The case study will focus on local agricultural mixed system specifically the Tilapia fish and the fonio plant. Despite the regulated use of pesticides for agriculture their wide use in the country is still problematic.

26
PARTNERS
16
COUNTRIES
€ 5 015 233,25
EU CONTRIBUTION
Latest News
URBANE 🇪🇺 and CIRAD 🇧🇯 discussion collaboration 🥬
📅 June 2025 📍 Republic du Benin 🤝 URBANE project & CIRAD (Centre de coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le développement) We are pleased to announce we had fruitful[…]
Read more🌱 Improved clearing: An agroecological practice serving the land 🌿
Improved clearing is a simple and effective method that helps restore the soil while increasing agricultural productivity. It involves conserving and selecting a few young tree shoots during field preparation,[…]
Read more
M36 Consortium meeting – Benin 🇧🇯
Greetings from Benin! URBANE’s M36 Consortium meeting is taking place in Cotonou, Benin. Important updates from our 6 Case Studies delivered with excellent results from the work on #synbiotics and[…]
Read moreResults
Find all our published and publicly available work that form part of our project results.

Applications of Probiotic-Based Multi-Components to Human, Animal and Ecosystem Health: Concepts, Methodologies, and Action Mechanisms
Microorganisms
24 August 2022
learn more
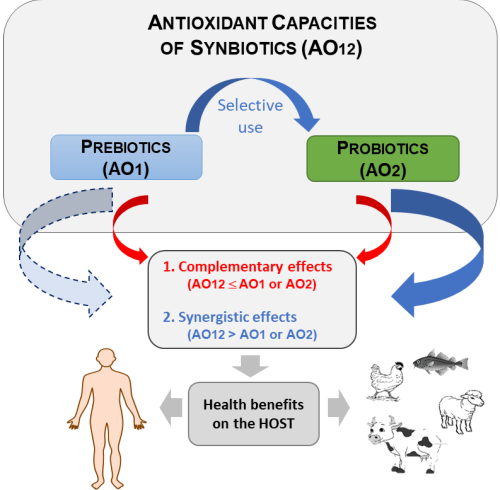
Synbiotics and their Antioxidant Properties, Mechanisms, and Benefits on Human and Animal Health: A Narrative Review
Biomolecules
09 October 2022
learn more

Nature-Based One Health Approaches to Urban Agriculture Can Deliver Food and Nutrition Security
Frontiers in Nutrition “Sec. Nutrition and Sustainable Diets “
11 March 2022
learn more
Probiotics as antibiotic alternatives for human and animal applications
Encyclopedia
30 April 2023
learn more
Sign up to our newsletter!
Fill in the form below to sign up to receiving news about URBANE



























